The Pythagorean theorem
The Pythagorean theorem was reportedly formulated by the Greek mathematician and philosopher Pythagoras of Samos in the 6th century BC. It says that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse of the triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs of the triangle. If you write it in the form of an equation, it looks like this:
a2 + b2 = c2
In this equation, c represents the length of the hypotenuse, while the legs are represented by a and b.
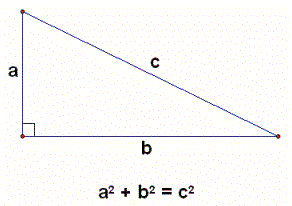
In this form, the Pythagorean theorem enables you to find the length of any side in a right triangle if you know the other two, as well as to check if a triangle is a right triangle. This proves quite useful in solving math problems during education, as well as in a number of real life situations. We are going to illustrate this through these few examples:
Example 1
The length of one side is 9 cm and the length of the other side is 10 cm. Calculate the length of the hypotenuse.
This is a very simple problem. We know the length of two sides of the triangle and to determine the length of the hypotenuse, we just have to insert the lengths we know into the equation.
c2 = a2 + b2
c2 = 92 + 102
c2 = 81 + 100
c2 = 181
c = 13,5 cm
We see now that the missing length of the hypotenuse is 13,5 cm and that is our result. The next assignment will be a bit more complicated.
Example 2
The length of the hypotenuse is 10,6 cm and the length of one of the legs is 5,2 cm. Find the length of the other leg of the triangle.
This is also very simple. Let us name the hypotenuse c and the side we already know – a. The missing side is b. To get b from our equation we need to rearrange it a bit. Like this:
b2 = c2 – a2
The only thing left to do now is to insert the known values into the equation.
b2 = 10,62 – 5,22
b2 = 112,36 – 27,04
b2 = 85,32
b = 9,2 cm
The length of the missing side is 9,2 cm. Now let us take a look at one more example.
Example 3
The length of the hypotenuse is 6,5 cm, the length of leg a is 5,6 cm and the length of leg b is 3,3. Do these sides belong to a right triangle?
As before, this can also be solved easily. We will take the lengths of two sides of the triangle in question, calculate the length of the third using the Pythagorean theorem and check if our result is a match to the length of the hypotenuse of our triangle. We will do it like this:
c2 = 5,62 + 3,32
c2 = 42,25
c = 6,5 cm
As we can see, the length we calculated if identical to the given length of this triangle. This means that the triangle in question is indeed a right triangle.
These are just some of the numerous uses of the Pythagorean theorem. If you wish to practice working with the Pythagorean theorem, please feel free to use the math worksheets below.
Pythagorean theorem exams for teachers
| Exam Name | File Size | Downloads | Upload date |
|
Integers
|
|||
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – very easy | 456.4 kB | 27722 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – easy | 590.8 kB | 21433 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – medium | 592.9 kB | 32139 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – hard | 594.5 kB | 18493 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – very hard | 607 kB | 14179 | September 3, 2019 |
|
Decimals
|
|||
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – very easy | 456.4 kB | 5749 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – easy | 599.4 kB | 4292 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – medium | 596 kB | 6632 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – hard | 599.2 kB | 5334 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – vey hard | 605.9 kB | 6055 | September 3, 2019 |
Pythagorean theorem worksheets for students
| Worksheet Name | File Size | Downloads | Upload date |
|
Integers
|
|||
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – Find the missing hypotenuse | 3.4 MB | 78308 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – Find the missing leg | 3.4 MB | 41317 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – Find the missing parameter | 3.3 MB | 16313 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Integers – Right triangle or not | 2.8 MB | 19845 | September 3, 2019 |
|
Decimals
|
|||
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – Find the missing hypotenuse | 7.1 MB | 7925 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – Find the missing leg | 7.2 MB | 5953 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – Find the missing parameter | 7.1 MB | 6640 | September 3, 2019 |
| Pythagorean theorem – Decimals – Right triangle or not | 7.6 MB | 5753 | September 3, 2019 |